Non-Surgical Burning or Freezing of Tumors/Microwave & Cryoablation
What is Microwave & Cryoablation?
Microwave and Cryoablation are percutaneous ablations that are used to treat tumors in the liver, kidney, bone, soft tissue and other locations, allowing minimally invasive destruction of tumors without the need for open surgery.
How are Microwave & Cryoablation Performed?
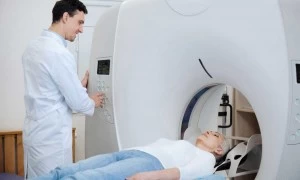
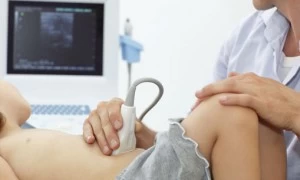
With the patient under conscious sedation or general anesthesia, an interventional radiology physician uses ultrasound, CT, or a combination of both, to guide specialized needles into the tumor. The needles use heat (microwave ablation) and cold (cryoablation) to kill the tumor without requiring open surgery.
What are the Risks of Microwave & Cryoablation?
Bleeding, infection, damage to surrounding structures, organ damage, and rare tumor seeding can be associated with this procedure.
Post Procedure & Follow Up
After ablation, patients proceed to the post-anesthesia care unit for recovery. A post-procedure imaging scan may be performed to determine the effect of the ablation. Most patients are discharged home the same day. Antibiotics and/or pain medications may be prescribed to prevent pain or infection after the procedure.
A follow-up CT or MRI is usually performed after treatment along with clinic visit in interventional radiology to determine the results and allow for further treatment planning.